tUniqRow
Ensures data quality of input or output flow in a Job.
Compares entries and sorts out duplicate entries from the input flow.
Depending on the Talend solution you
are using, this component can be used in one, some or all of the following Job
frameworks:
-
Standard: see tUniqRow Standard properties.
The component in this framework is generally available.
-
MapReduce: see tUniqRow MapReduce properties.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to one
of the
Talend
solutions with Big Data. -
Spark Batch: see tUniqRow properties for Apache Spark Batch.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to one
of the
Talend
solutions with Big Data. -
Spark Streaming: see tUniqRow properties for Apache Spark Streaming.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to Talend Real-time Big Data Platform or Talend Data
Fabric.
tUniqRow Standard properties
These properties are used to configure tUniqRow running in the Standard Job framework.
The Standard
tUniqRow component belongs to the Data Quality family.
The component in this framework is generally available.
Basic settings
|
Schema and Edit |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields (columns) to Click Edit schema to make changes to the schema.
This component offers the This dynamic schema |
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the |
|
|
Repository: You have already created |
|
Unique key |
In this area, select one or more columns to carry out – Select the Key attribute check – Select the Case sensitive |
Advanced settings
|
Only once each duplicated key |
Select this check box if you want to have only the first |
|
Use of disk (suitable for processing large row set) |
Select this check box to enable generating temporary files on the – Buffer size in memory: Select – Directory for temp files: Set Warning:
Make sure that you specify an existing directory for |
|
Ignore trailing zeros for |
Select this check box to ignore trailing zeros for BigDecimal |
|
tStatCatcher Statistics |
Select this check box to gather the job processing metadata at a job level as well as |
Global Variables
|
Global Variables |
NB_UNIQUES: the number of unique rows. This is an After
NB_DUPLICATES: the number of duplicate rows. This is an
ERROR_MESSAGE: the error message generated by the A Flow variable functions during the execution of a component while an After variable To fill up a field or expression with a variable, press Ctrl + For further information about variables, see |
Usage
|
Usage rule |
This component handles flow of data therefore it requires input |
Scenario 1: Deduplicating entries
In this five-component Job, we will sort entries on an input name list, find out
duplicated names, and display the unique names and the duplicated names on the Run console.

Setting up the Job
-
Drop a tFileInputDelimited, a tSortRow, a tUniqRow, and two tLogRow
components from the Palette to the design
workspace, and name the components as shown above. -
Connect the tFileInputDelimited
component, the tSortRow component, and the
tUniqRow component using Row > Main
connections. -
Connect the tUniqRow component and the
first tLogRow component using a Main > Uniques connection. -
Connect the tUniqRow component and the
second tLogRow component using a Main > Duplicates connection.
Configuring the components
-
Double-click the tFileInputDelimited
component to display its Basic settings
view.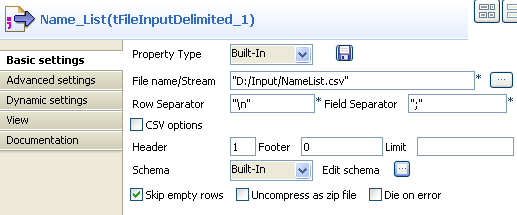
-
Click the […] button next to the
File Name field to browse to your input
file. -
Define the header and footer rows. In this use case, the first row of the
input file is the header row. -
Click Edit schema to define the schema
for this component. In this use case, the input file has five columns:
Id, FirstName,
LastName, Age, and
City. Then click OK to propagate the schema and close the schema
editor. -
Double-click the tSortRow component to
display its Basic settings view.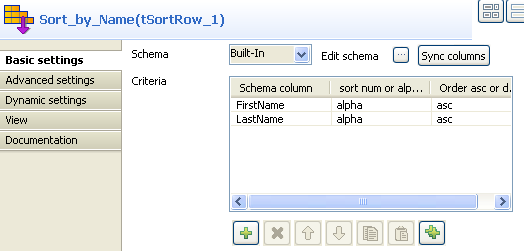
-
To rearrange the entries in the alphabetic order of the names, add two
rows in the Criteria table by clicking the
plus button, select the FirstName and
LastName columns under Schema
column, select alpha as the sorting
type, and select the sorting order. -
Double-click the tUniqRow component to
display its Basic settings view.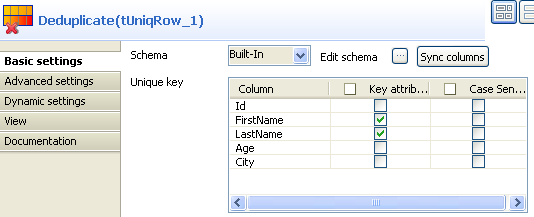
-
In the Unique key area, select the
columns on which you want deduplication to be carried out. In this use case,
you will sort out duplicated names. -
In the Basic settings view of each of the
tLogRow components, select the
Table option to view the Job execution
result in table mode.
Saving and executing the Job
- Press Ctrl+S to save your Job.
-
Run the Job by pressing F6 or clicking
the Run button on the Run tab.The unique names and duplicated names are displayed in different tables on
the Run console.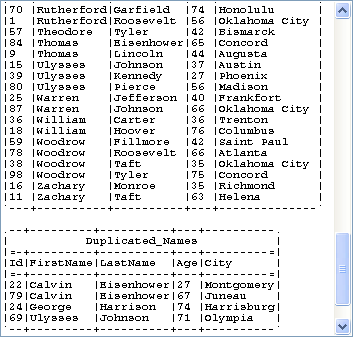
Scenario 2: Deduplicating entries based on dynamic schema
This scenario applies only to a subscription-based Talend Platform solution or Talend Data Fabric.
In this use case, we will use a Job similar to the one in the scenario described
earlier to deduplicate the input entries about several families, so that only one person
per family stays on the name list. As all the components in this Job support the dynamic
schema feature, we will leverage this feature to save the time of configuring individual
columns of the schemas.

Setting up the Job
-
Drop these components from the Palette to
the design workspace: tFileInputDelimited,
tExtractDynamicFields, tUniqRow, tFileOutputDelimited, and tLogRow, and name the components as shown above to better
identify their roles in the Job. -
Connect the component labelled People,
the component labelled Split_Column, and
the component labelled Deduplicate using
Row > Main connections. -
Connect the component labelled Deduplicate and the component labelled Unique_Families using a Main > Uniques
connection. - Connect the component labelled Deduplicate and the component labelled Duplicated_Families using a Main > Duplicates connection.
Configuring the components
-
Double-click the component labelled People to display its Basic
settings view.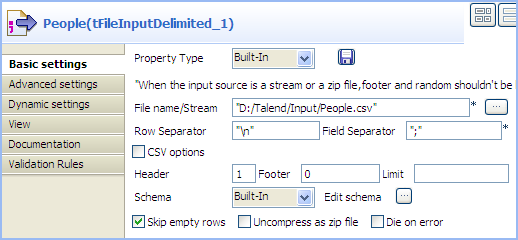 Warning:
Warning:The dynamic schema feature is only supported in Built-In mode and requires the input file
to have a header row. -
Click the […] button next to the
File Name/Stream field to browse to
your input file. -
Define the header and footer rows. In this use case, the first row of the
input file is the header row. -
Click Edit schema to define the schema
for this component.In this use case, the input file has five columns:
FirstName, LastName,
HouseNo, Street,
and City. However, as we can leverage the advantage of
the dynamic schema feature, we simply define one dynamic column in the
schema, Dyna in this example.To do so :- Add a new line by clicking the [+] button.
- Type Dyna in the Column field.
-
Select Dynamic from the Type list.
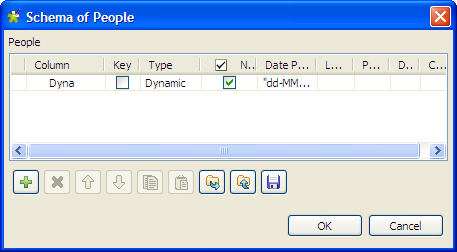
-
Then, click OK to propagate the
schema and close the [Schema]
dialog box.
-
Double-click the component labelled Split_Column to display its Basic
settings view.We will use this component to split the dynamic column of the input schema
into two columns, one for the first name and the other for the family
related information. To do so:-
Click Edit schema to open the
[Schema] dialog box.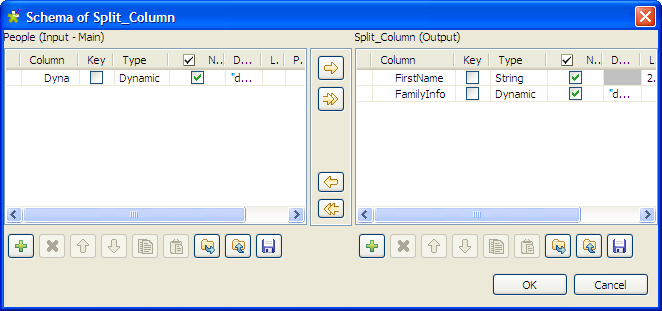
-
In the output panel, click the [+] button to add two columns for the output schema,
and name them FirstName and
FamilyInfo
respectively. -
Select String from the Type list for the FirstName column to extract this column from the
input schema to carry the first name of each person on the name
list. -
Select Dynamic from the Type list for the FamilyInfo column so that this column will carry the
rest information of each person on the name list: the last name,
house number, street and city, which all together will identify a
family. -
Then, click OK to propagate the
schema and close the [Schema]
dialog box.
-
Click Edit schema to open the
-
Double-click the component labelled Deduplicate to display its Basic
settings view.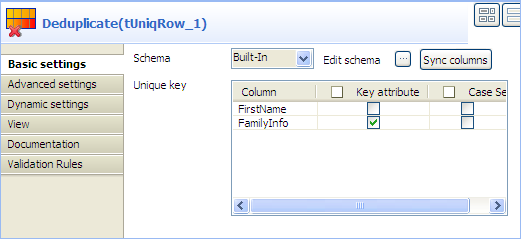
-
In the Unique key area, select the
Key attribute check box for the
FamilyInfo column to carry out
deduplication on the family information. -
In the Basic settings view of the
tFileOutputDelimited component, which
is labelled Deduplicated_Families, define
the output file path, select the Include
header check box, and leave the other settings as they
are.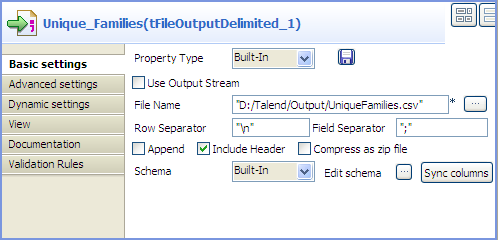
-
In the Basic settings view of the
tLogRow component, which is labelled
Duplicated_Families, select the
Table option to view the Job execution
result in table mode.
Saving and executing the Job
- Press Ctrl+S to save your Job.
-
Run the Job by pressing F6 or clicking
the Run button on the Run tab.The information of duplicated families is displayed on the Run console, and only one person per family stays
on the name list in the output file.
tUniqRow MapReduce properties
These properties are used to configure tUniqRow running in the MapReduce Job framework.
The MapReduce
tUniqRow component belongs to the Data Quality family.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to one
of the
Talend
solutions with Big Data.
Basic settings
|
Schema et Edit |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields (columns) to Click Edit schema to make changes to the schema.
This component offers the This dynamic schema |
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the |
|
|
Repository: You have already created |
|
Unique key |
In this area, select one or more columns to carry out – Select the – Select the Case sensitive check box to differentiate upper case |
Advanced settings
|
Only once each duplicated key |
Select this check box if you want to have only the |
|
Ignore trailing zeros for |
Select this check box to ignore trailing zeros for |
Global
Variables
|
Global |
ERROR_MESSAGE: the error message generated by the A Flow variable functions during the execution of a component while an After variable To fill up a field or expression with a variable, press Ctrl + For further information about variables, see |
Usage
|
Usage rule |
In a For further information about a For a scenario demonstrating a Map/Reduce Job using this component, Note that in this documentation, unless otherwise |
Scenario: Deduplicating entries using Map/Reduce components
This scenario applies only to a subscription-based Talend Platform solution with Big data or Talend Data Fabric.
This scenario illustrates how to create a
Talend
Map/Reduce Job to
deduplicate entries, that is to say, to use Map/Reduce components to generate Map/Reduce
code and run the Job right in Hadoop.
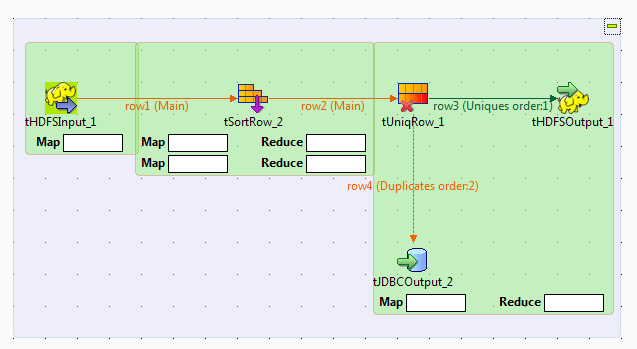
Note that the
Talend
Map/Reduce components are available to
subscription-based Big Data users only and this scenario can be replicated only with
Map/Reduce components.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
1;Harry;Ford;68;Albany 2;Franklin;Wilson;79;Juneau 3;Ulysses;Roosevelt;25;Harrisburg 4;Harry;Ford;48;Olympia 5;Martin;Reagan;75;Columbia 6;Woodrow;Roosevelt;63;Harrisburg 7;Grover;McKinley;98;Atlanta 8;John;Taft;93;Montpelier 9;Herbert;Johnson;85;Lincoln 10;Grover;McKinley;33;Lansing |
Since
Talend Studio
allows you to convert a Job between its
Map/Reduce and Standard (Non Map/Reduce) versions, you can convert the scenario
explained earlier to create this Map/Reduce Job. This way, many components used can keep
their original settings so as to reduce your workload in designing this Job.
Before starting to replicate this scenario, ensure that you have appropriate rights
and permissions to access the Hadoop distribution to be used. Then proceed as
follows:
Converting the Job
-
In the Repository tree view of the
Integration
perspective of
Talend Studio
,
right-click the Job you have created in the earlier scenario to open its
contextual menu and select Edit
properties.Then the [Edit properties] dialog box is
displayed. Note that the Job must be closed before you are able to make any
changes in this dialog box.This dialog box looks like the image below:
 Note that you can change the Job name as well as the other descriptive
Note that you can change the Job name as well as the other descriptive
information about the Job from this dialog box. -
From the Job Type list, select Big Data Batch. Then a Map/Reduce Job using the same
name appears under the Big Data Batch sub-node
of the Job Design node.
Rearranging the components
-
Double-click this new Map/Reduce Job to open it in the workspace. The Map/Reduce
components’ Palette is opened accordingly
and in the workspace, the crossed-out components, if any, indicate that
those components do not have the Map/Reduce version. - Right-click each of those components in question and select Delete to remove them from the workspace.
-
Drop a tHDFSInput component, a tHDFSOutput component and a tJDBCOutput component in the workspace. The tHDFSInput component reads data from the Hadoop
distribution to be used, the tHDFSOutput
component writes data in that distribution and the tJDBCOutput component writes data in a given database, for
example, a MySQL database in this scenario. The two output components
replace the two tLogRow components to
output data.If from scratch, you have to drop a tSortRow component and a tUniqRow component, too. -
Connect tHDFSInput to tSortRow using the Row >
Main link and accept to get the schema of tSortRow. -
Connect tUniqRow to tHDFSOutput using Row >
Uniques and to tJDBCOutput
using Row > Duplicates.
Setting up Hadoop connection
-
Click Run to open its view and then click the
Hadoop Configuration tab to display its
view for configuring the Hadoop connection for this Job. -
From the Property type list,
select Built-in. If you have created the
connection to be used in Repository, then
select Repository and thus the Studio will
reuse that set of connection information for this Job. -
In the Version area, select the
Hadoop distribution to be used and its version.If you cannot find from the list the distribution corresponding to yours,
select Custom so as to connect to a
Hadoop distribution not officially supported in the Studio. For a
step-by-step example about how to use this Custom option, see Connecting to a custom Hadoop distribution.If you use Google Cloud Dataproc, see Defining the Dataproc connection parameters for MapReduce Jobs.
Along with the evolution of Hadoop, please note the following changes:-
If you use Hortonworks Data
Platform V2.2, the configuration files of your
cluster might be using environment variables such as ${hdp.version}. If this is your situation,
you need to set the mapreduce.application.framework.path property in the
Hadoop properties table
with the path value explicitly pointing to the MapReduce
framework archive of your cluster. For
example:1mapreduce.application.framework.path=/hdp/apps/2.2.0.0-2041/mapreduce/mapreduce.tar.gz#mr-framework -
If you use Hortonworks Data
Platform V2.0.0, the type of the operating
system for running the distribution and a
Talend
Job must be the same, such as Windows or Linux.
Otherwise, you have to use
Talend
Jobserver to execute the Job in the same type of
operating system in which the Hortonworks Data Platform V2.0.0 distribution
you are using is run.
-
-
In the Name node field, enter the location of
the master node, the NameNode, of the distribution to be used. For example,
hdfs://tal-qa113.talend.lan:8020.-
If you are using a MapR distribution, you can simply leave maprfs:/// as it is in this field; then the MapR
client will take care of the rest on the fly for creating the connection. The
MapR client must be properly installed. For further information about how to set
up a MapR client, see the following link in MapR’s documentation: http://doc.mapr.com/display/MapR/Setting+Up+the+Client -
If you are using WebHDFS, the location should be
webhdfs://masternode:portnumber; if this WebHDFS is secured
with SSL, the scheme should be swebhdfs and you need to use
a tLibraryLoad in the Job to load the library required by
the secured WebHDFS.
-
-
In the Resource Manager field,
enter the location of the ResourceManager of your distribution. For example,
tal-qa114.talend.lan:8050.-
Then you can continue to set the following parameters depending on the
configuration of the Hadoop cluster to be used (if you leave the check
box of a parameter clear, then at runtime, the configuration about this
parameter in the Hadoop cluster to be used will be ignored):-
Select the Set resourcemanager
scheduler address check box and enter the Scheduler address in
the field that appears. -
Select the Set jobhistory
address check box and enter the location of the JobHistory
server of the Hadoop cluster to be used. This allows the metrics information of
the current Job to be stored in that JobHistory server. -
Select the Set staging
directory check box and enter this directory defined in your
Hadoop cluster for temporary files created by running programs. Typically, this
directory can be found under the yarn.app.mapreduce.am.staging-dir property in the configuration files
such as yarn-site.xml or mapred-site.xml of your distribution. -
Select the Use datanode
hostname check box to allow the Job to access datanodes via
their hostnames. This actually sets the dfs.client.use.datanode.hostname property to true. When connecting to a S3N filesystem, you must select this check
box.
-
-
-
If you are accessing the Hadoop cluster running
with Kerberos security, select this check box, then, enter the Kerberos
principal name for the NameNode in the field displayed. This enables you to use
your user name to authenticate against the credentials stored in Kerberos.
-
If this cluster is a MapR cluster of the version 4.0.1 or later, you can set the MapR
ticket authentication configuration in addition or as an alternative by following the
explanation in Connecting to a security-enabled MapR.Keep in mind that this configuration generates a new MapR security ticket for the username
defined in the Job in each execution. If you need to reuse an existing ticket issued for the
same username, leave both the Force MapR ticket
authentication check box and the Use Kerberos
authentication check box clear, and then MapR should be able to automatically
find that ticket on the fly.
In addition, since this component performs Map/Reduce computations, you
also need to authenticate the related services such as the Job history server and
the Resource manager or Jobtracker depending on your distribution in the
corresponding field. These principals can be found in the configuration files of
your distribution. For example, in a CDH4 distribution, the Resource manager
principal is set in the yarn-site.xml file and the Job history
principal in the mapred-site.xml file.If you need to use a Kerberos keytab file to log in, select Use a keytab to authenticate. A keytab file contains
pairs of Kerberos principals and encrypted keys. You need to enter the principal to
be used in the Principal field and the access
path to the keytab file itself in the Keytab
field. This keytab file must be stored in the machine in which your Job actually
runs, for example, on a Talend
Jobserver.Note that the user that executes a keytab-enabled Job is not necessarily
the one a principal designates but must have the right to read the keytab file being
used. For example, the user name you are using to execute a Job is user1 and the principal to be used is guest; in this
situation, ensure that user1 has the right to read the keytab
file to be used. -
-
In the User name field, enter the login user
name for your distribution. If you leave it empty, the user name of the machine
hosting the Studio will be used. -
In the Temp folder field, enter the path in
HDFS to the folder where you store the temporary files generated during
Map/Reduce computations. -
Leave the default value of the Path separator in
server as it is, unless you have changed the separator used by your
Hadoop distribution’s host machine for its PATH variable or in other words, that
separator is not a colon (:). In that situation, you must change this value to the
one you are using in that host.
-
Leave the Clear temporary folder check box
selected, unless you want to keep those temporary files. -
Leave the Compress intermediate map output to reduce
network traffic check box selected, so as to spend shorter time
to transfer the mapper task partitions to the multiple reducers.However, if the data transfer in the Job is negligible, it is recommended to
clear this check box to deactivate the compression step, because this
compression consumes extra CPU resources. -
If you need to use custom Hadoop properties, complete the Hadoop properties table with the property or
properties to be customized. Then at runtime, these changes will override the
corresponding default properties used by the Studio for its Hadoop
engine.For further information about the properties required by Hadoop, see Apache’s
Hadoop documentation on http://hadoop.apache.org, or
the documentation of the Hadoop distribution you need to use. -
If the HDFS transparent encryption has been enabled in your cluster, select
the Setup HDFS encryption configurations check
box and in the HDFS encryption key provider field
that is displayed, enter the location of the KMS proxy.
For further information about the HDFS transparent encryption and its KMS proxy, see Transparent Encryption in HDFS.
-
If the Hadoop distribution to be used is Hortonworks Data Platform V1.2 or Hortonworks
Data Platform V1.3, you need to set proper memory allocations for the map and reduce
computations to be performed by the Hadoop system.
In that situation, you need to enter the values you need in the Mapred
job map memory mb and the Mapred job reduce memory
mb fields, respectively. By default, the values are both 1000 which are normally appropriate for running the
computations.If the distribution is YARN, then the memory parameters to be set become Map (in Mb), Reduce (in Mb) and
ApplicationMaster (in Mb), accordingly. These fields
allow you to dynamically allocate memory to the map and the reduce computations and the
ApplicationMaster of YARN.For further information about the Resource Manager, its scheduler and the
ApplicationMaster, see YARN’s documentation such as http://hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-concepts-and-applications/.For further information about how to determine YARN and MapReduce memory configuration
settings, see the documentation of the distribution you are using, such as the following
link provided by Hortonworks: http://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP2/HDP-2.0.6.0/bk_installing_manually_book/content/rpm-chap1-11.html. -
If you are using Cloudera V5.5+, you can select the Use Cloudera Navigator check box to enable the Cloudera Navigator of your
distribution to trace your Job lineage to the component level, including the schema
changes between components.
With this option activated, you need to set the following parameters:
-
Username and Password: this is the credentials you use to connect to your Cloudera
Navigator. -
Cloudera Navigator URL : enter the location
of the Cloudera Navigator to be connected to. -
Cloudera Navigator Metadata URL: enter the
location of the Navigator Metadata. -
Activate the autocommit option: select this
check box to make Cloudera Navigator generate the lineage of the current Job at the end
of the execution of this Job.Since this option actually forces Cloudera Navigator to generate lineages of
all its available entities such as HDFS files and directories, Hive queries or Pig
scripts, it is not recommended for the production environment because it will slow the
Job. -
Kill the job if Cloudera Navigator fails: select this check
box to stop the execution of the Job when the connection to your Cloudera Navigator fails.Otherwise, leave it clear to allow your Job to continue to run.
-
Disable SSL validation: select this check box to
make your Job to connect to Cloudera Navigator without the SSL validation
process.This feature is meant to facilitate the test of your Job but is not
recommended to be used in a production cluster.
-
-
If you are using Hortonworks Data Platform V2.4.0 onwards and you have
installed Atlas in your cluster, you can select the Use
Atlas check box to enable Job lineage to the component level, including the
schema changes between components.
With this option activated, you need to set the following parameters:
-
Atlas URL : enter the location of the Atlas
to be connected to. It is often http://name_of_your_atlas_node:port -
Die on error: select this check box to stop the Job
execution when Atlas-related issues occur, such as connection issues to Atlas.Otherwise, leave it clear to allow your Job to continue to run.
In the Username field and the Password field, enter the authentication information for access
to Atlas. -
Configuring input and output components
Configuring tHDFSInput
-
Double-click tHDFSInput to open its
Component view.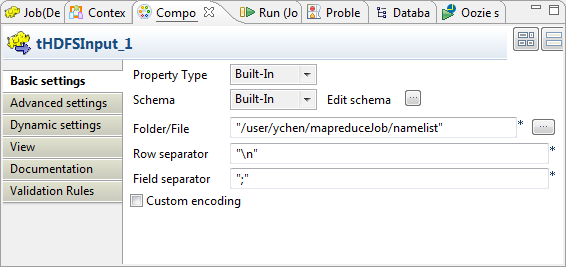
-
Click the

button next to Edit
schema to verify that the schema received in the earlier
steps is properly defined.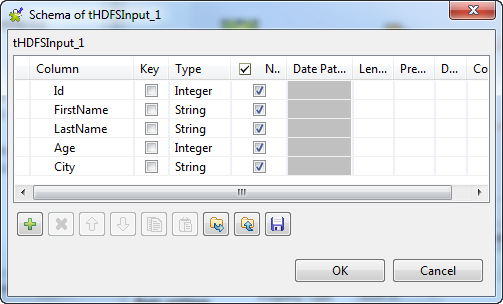 Note that if you are creating this Job from scratch, you need to click the
Note that if you are creating this Job from scratch, you need to click the
button to manually add these schema columns; otherwise,
if the schema has been defined in Repository, you can select the Repository option from the Schema list in the Basic
settings view to reuse it. For further information about how
to define a schema in Repository, see the
chapter describing metadata management in the
Talend Studio User Guide or the chapter describing the
Hadoop cluster node in Repository of the Getting Started Guide. -
If you make changes in the schema, click OK to validate these changes and accept the propagation
prompted by the pop-up dialog box. -
In the Folder/File field, enter the path,
or browse to the source file you need the Job to read.If this file is not in the HDFS system to be used, you have to place it in
that HDFS, for example, using tFileInputDelimited and tHDFSOutput in a Standard
Job.
Reviewing the transformation components
-
Double-click tSortRow to open its
Component view.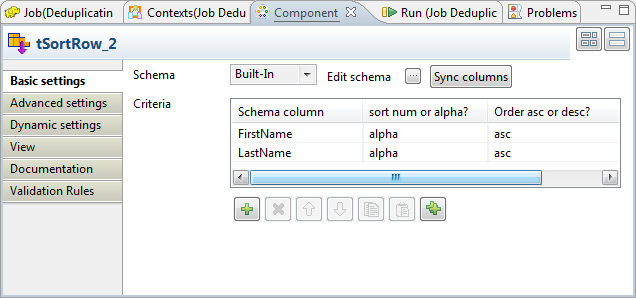 This component keeps its configuration used by the original Job. It sorts
This component keeps its configuration used by the original Job. It sorts
the incoming entries into alphabetical order depending on the FirstName and the LastName columns. -
Double-click tUniqRow to open its
Component view.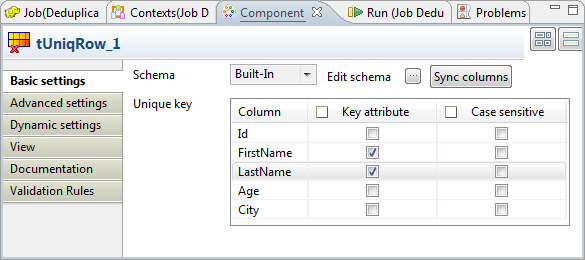 The component keeps as well its configuration from the original Job. It
The component keeps as well its configuration from the original Job. It
separates the incoming entries into a Uniques flow and a Duplicates flow, then sends the unique entries to tHDFSOutput and the duplicate entries to
tJDBCOutput.
Configuring tHDFSOutput
-
Double-click tHDFSOutput to open its
Component view.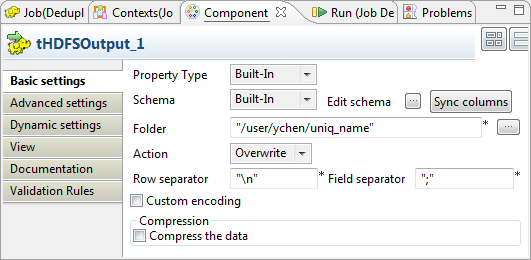
-
As explained earlier for verifying the schema of tHDFSInput, do the same to verify the schema of tHDFSOutput. If it is not consistent with that of
its preceding component, tUniqRow, click
Sync column to retrieve the schema of
tUniqRow.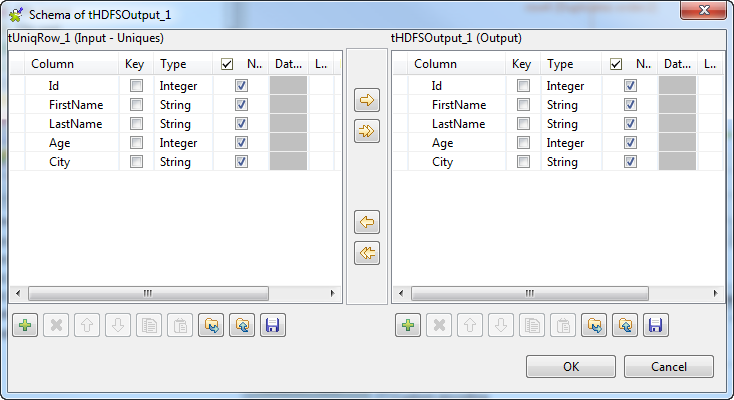
-
In the Folder field, enter the path, or
browse to the folder you want to write the unique entries in. -
From the Action list, select the
operation you need to perform on the folder in question. If the folder
already exists, select Overwrite;
otherwise, select Create.
Configuring tJDBCOutput
-
Double-click tJDBCOutput to open its
Component view.
-
In the JDBC URL field, enter the URL of
the database in which you need to write the duplicate entries. In this
example, it is jdbc:mysql://10.42.10.13:3306/Talend, a MySQL database
called Talend. -
In the Drive JAR table, add one row to
the table by clicking the
button.
-
Click this new row and then click the

button to open the [Select
Module] dialog box from which to import the jar file required
by the MySQL database.
-
In the Class name field, enter the class
file to be called. In this example, it is org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver. -
In the User name and the Password fields, enter the authentication
information to that database. -
In the Table name field, enter the name
of the table in which you need to write data, for example, Namelist. This table must already exist.
Executing the Job
Then you can press F6 to run this Job.
Once done, view the execution results in the web console of HDFS and in the MySQL
database.
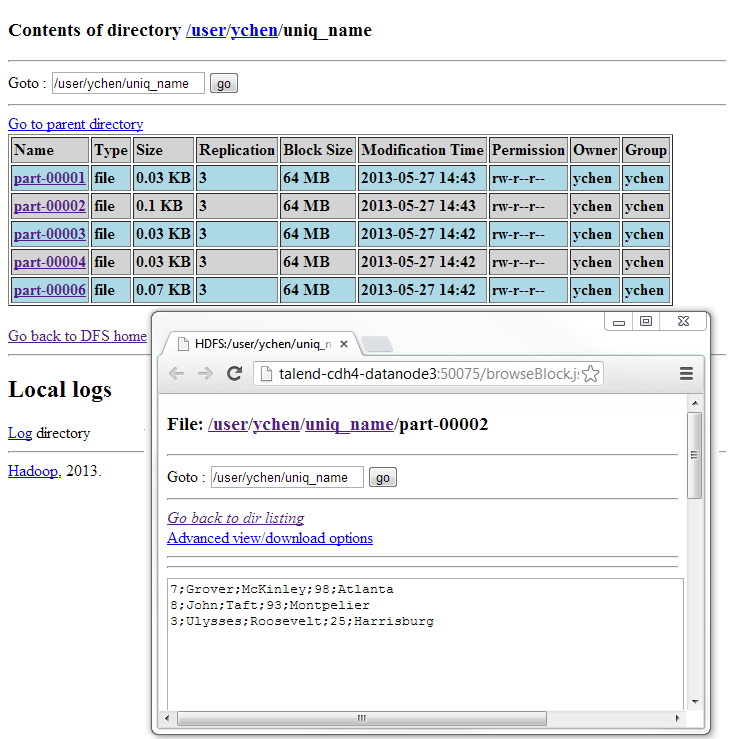
In HDFS, the unique entries are written in split files.
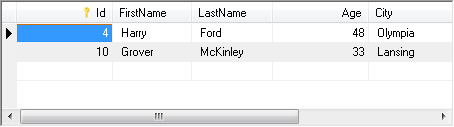
In MySQL, two duplicate entries are entered.
If you need to obtain more details about the Job, it is recommended to use the web
console of the Jobtracker provided by the Hadoop distribution you are using.
tUniqRow properties for Apache Spark Batch
These properties are used to configure tUniqRow running in the Spark Batch Job framework.
The Spark Batch
tUniqRow component belongs to the Processing family.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to one
of the
Talend
solutions with Big Data.
Basic settings
|
Schema and Edit schema |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields (columns) to Click Edit schema to make changes to the schema.
|
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the |
|
|
Repository: You have already created |
|
Unique key |
In this area, select one or more columns to carry out deduplication on – Select the Key attribute check box – Select the Case sensitive check |
Advanced settings
|
Only once each duplicated key |
Select this check box if you want to have only the first duplicated |
Usage
|
Usage rule |
This component is used as an intermediate step. This component, along with the Spark Batch component Palette it belongs to, appears only Note that in this documentation, unless otherwise |
|
Spark Connection |
You need to use the Spark Configuration tab in
the Run view to define the connection to a given Spark cluster for the whole Job. In addition, since the Job expects its dependent jar files for execution, you must specify the directory in the file system to which these jar files are transferred so that Spark can access these files:
This connection is effective on a per-Job basis. |
Related scenarios
No scenario is available for the Spark Batch version of this component
yet.
tUniqRow properties for Apache Spark Streaming
These properties are used to configure tUniqRow running in the Spark Streaming Job framework.
The Spark Streaming
tUniqRow component belongs to the Processing family.
The component in this framework is available only if you have subscribed to Talend Real-time Big Data Platform or Talend Data
Fabric.
Basic settings
|
Schema et Edit schema |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields (columns) to Click Edit schema to make changes to the schema.
|
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the |
|
|
Repository: You have already created |
|
Unique key |
In this area, select one or more columns to carry out deduplication on – Select the Key attribute check box – Select the Case sensitive check |
Advanced settings
|
Only once each duplicated key |
Select this check box if you want to have only the first duplicated |
Usage
|
Usage rule |
This component is used as an intermediate step. This component, along with the Spark Streaming component Palette it belongs to, appears Note that in this documentation, unless otherwise explicitly stated, a scenario presents |
|
Spark Connection |
You need to use the Spark Configuration tab in
the Run view to define the connection to a given Spark cluster for the whole Job. In addition, since the Job expects its dependent jar files for execution, you must specify the directory in the file system to which these jar files are transferred so that Spark can access these files:
This connection is effective on a per-Job basis. |
Related scenarios
No scenario is available for the Spark Streaming version of this component
yet.