![]()
|
Component family |
Databases/MySQL |
|
|
Function |
tMysqlInput reads a database and |
|
|
Purpose |
tMysqlInput executes a DB query |
|
|
Basic settings |
Property type |
Either Built-in or Since version 5.6, both the Built-In mode and the Repository mode are |
|
|
|
Built-in: No property data stored |
|
|
|
Repository: Select the repository |
|
|
|
Click this icon to open a database connection wizard and store the For more information about setting up and storing database |
|
|
Use an existing connection |
Select this check box and in the Component List click the NoteWhen a Job contains the parent Job and the child Job, if you need to share an existing
For an example about how to share a database connection across Job levels, see |
|
|
Host |
Database server IP address. |
|
|
Port |
Listening port number of DB server. |
|
|
Database |
Name of the database. |
|
|
Username and |
DB user authentication data. To enter the password, click the […] button next to the |
|
|
Schema and Edit |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields to be processed and passed on Since version 5.6, both the Built-In mode and the Repository mode are This component offers the advantage of the dynamic schema feature. This allows you to This dynamic schema feature is designed for the purpose of retrieving unknown columns |
|
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the schema locally for this |
|
|
|
Repository: You have already created the schema and |
|
Click Edit schema to make changes to the schema. If the
|
||
|
|
Table |
Name of the table to be read. |
|
|
Query type and |
Enter your DB query paying particularly attention to properly Warning
If using the dynamic schema feature, the |
| Specify a data source alias |
Select this check box and specify the alias of a data source created on the Talend Runtime side to use the shared connection pool defined in the data source configuration. WarningIf you use the component’s own DB configuration, your data source connection will be This check box is not available when the Use an existing |
|
|
Advanced settings |
Additional JDBC parameters |
Specify additional connection properties for the DB connection you NoteWhen you need to handle data of the time-stamp type
|
|
|
Enable stream |
Select this check box to enables streaming over buffering which |
|
|
Trim all the String/Char columns |
Select this check box to remove leading and trailing whitespace |
|
|
Trim column |
Remove leading and trailing whitespace from defined NoteClear Trim all the String/Char |
|
|
tStatCatcher Statistics |
Select this check box to collect log data at the component |
|
Dynamic settings |
Click the [+] button to add a row in the table and fill The Dynamic settings table is available only when the For more information on Dynamic settings and context |
|
|
Global Variables |
NB_LINE: the number of rows processed. This is an After
QUERY: the SQL query statement being processed. This is a ERROR_MESSAGE: the error message generated by the A Flow variable functions during the execution of a component while an After variable To fill up a field or expression with a variable, press Ctrl + For further information about variables, see Talend Studio |
|
|
Usage |
This component covers all possible SQL queries for Mysql |
|
|
Log4j |
The activity of this component can be logged using the log4j feature. For more information on this feature, see Talend Studio User For more information on the log4j logging levels, see the Apache documentation at http://logging.apache.org/log4j/1.2/apidocs/org/apache/log4j/Level.html. |
|
In this scenario we will read certain columns from a MySQL database, and then write
them to a table in a local output file.
-
Drop tMysqlInput and tFileOutputDelimited from the Palette onto the workspace.
-
Link tMysqlInput to tFileOutputDelimited using a Row > Main connection.

-
Double-click tMysqlInput to open its
Basic Settings view in the Component tab.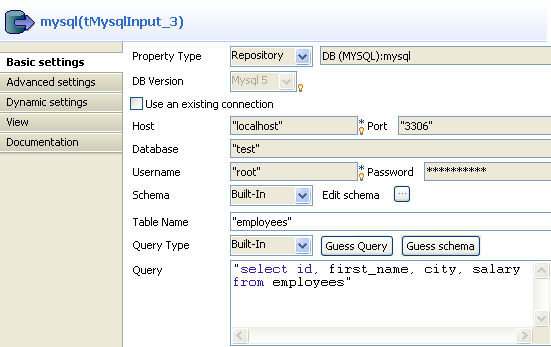
-
From the Property Type list, select
Repository if you have already stored
the connection to database in the Metadata
node of the Repository tree view. The
property fields that follow are automatically filled in.For more information about how to store a database connection, see
Talend Studio
User Guide.If you have not defined the database connection locally in the Repository, fill in the details manually after
selecting Built-in from the Property Type list. -
Set the Schema as Built-in and click Edit
schema to define the desired schema.The schema editor opens:
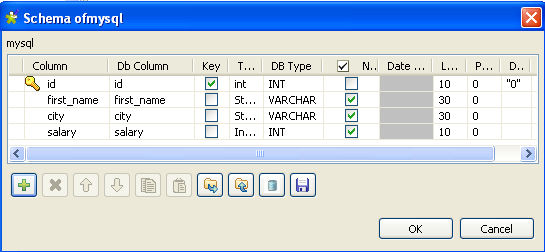
-
Click the [+] button to add the rows
that you will use to define the schema, four columns in this example
id, first_name,
city and salary.Under Column, click in the fields to
enter the corresponding column names.Click the field under Type to define the
type of data.Click OK to close the schema
editor. -
Next to the Table Name field, click
the […] button to select the database
table of interest.A dialog box displays a tree diagram of all the tables in the selected
database:
-
Click the table of interest and then click OK to close the dialog box.
-
Set the Query Type as Built-In.
-
In the Query box, enter the query
required to retrieve the desired columns from the table.
-
Double-click tFileOutputDelimited to set
its Basic settings in the Component tab.
-
Next to the File Name field, click the
[…] button to browse your directory
to where you want to save the output file, then enter a name for the
file.Select the Include Header check box to
retrieve the column names as well as the data. -
Save the Job.
The results below can be found after F6 is
pressed to run the Job.

As shown above, the output file is written with the desired column names and
corresponding data, retrieved from the database:
Note
The Job can also be run in the Traces Debug
mode, which allows you to view the rows as they are being written to the output
file, in the workspace.
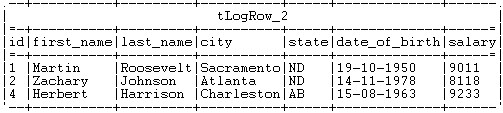
In this scenario, we will read a table from a MySQL database, using a context
parameter to refer to the table name.
-
Drop tMysqlInput and tLogRow from the Palette onto the workspace.
-
Link tMysqlInput to tLogRow using a Row >
Main connection.
-
Double-click tMysqlInput to open its
Basic Settings view in the Component tab.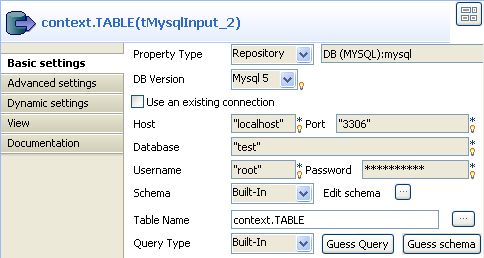
-
From the Property Type list, select
Repository if you have already stored
the connection to database in the Metadata
node of the Repository tree view. The
property fields that follow are automatically filled in.For more information about how to store a database connection, see
Talend Studio
User Guide.If you have not defined the database connection in the Repository, fill in the details manually after
selecting Built-in from the Property Type list. -
Set the Schema as Built-In and click Edit
schema to define the desired schema.The schema editor opens:

-
Click the [+] button to add the rows
that you will use to define the schema, seven columns in this example:
id, first_name, last_name, city, state, date_of_birth and salary.Under Column, click the fields to enter
the corresponding column names.Click the fields under Type to define
the type of data.Click OK to close the schema
editor. -
Put the cursor in the Table Name field
and press F5 for context parameter setting.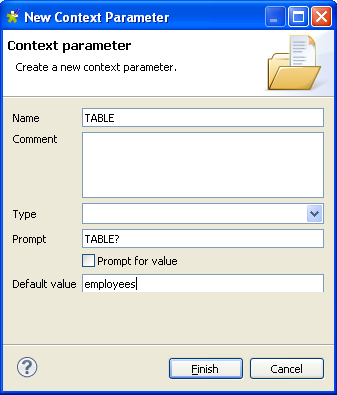
For more information about context settings, see Talend Studio
User Guide. -
Keep the default setting in the Name
field and type in the name of the database table in the Default value field, employees in this case. -
Click Finish to validate the setting.
The context parameter context.TABLE
automatically appears in the Table Name
field. -
In the Query type list, select Built-In. Then, click Guess
Query to get the query statement.In this use case, we want to read the records with the salary above 8000.
Therefore, we add aWhereclause and the final query statement
is as follows:1234567891011"SELECT"+context.TABLE+".`id`,"+context.TABLE+".`first_name`,"+context.TABLE+".`last_name`,"+context.TABLE+".`city`,"+context.TABLE+".`state`,"+context.TABLE+".`date_of_birth`,"+context.TABLE+".`salary`FROM "+context.TABLE+"WHERE"+context.TABLE+".`salary` > 8000" -
Double-click tLogRow to set its Basic Settings in the Component tab.

-
In the Mode area, select Table (print values in cells of a table) for a
better display of the results. -
Save the Job.
In this scenario we will read data from database tables with the same data structure
but in two different MySQL databases named project_q1
and project_q2 respectively. We will specify the
connections to these databases dynamically at runtime, without making any modification
to the Job.
-
Drop two tMysqlConnection, a tMysqlInput, a tLogRow, and a tMysqlClose
components onto the design workspace. -
Link the first tMysqlConnection to the
second tMysqlConnection and the second
tMysqlConnection to tMysqlInput using Trigger > On Subjob Ok
connections. -
Link tMysqlInput to tLogRow using a Row >
Main connection. -
Link tMysqlInput to tMysqlClose using a Trigger
> On Subjob Ok connection.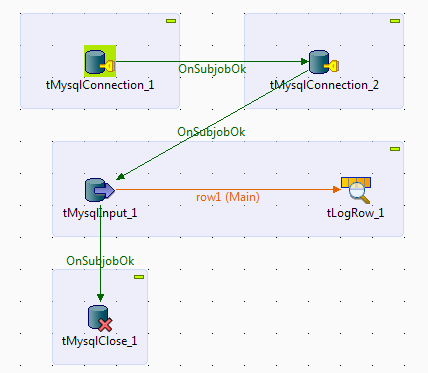
To be able to choose a database connection dynamically at runtime, we need to
define a context variable, which will then be configure it in the Dynamic settings of the database input component.
-
In the Contexts view, click the [+] button to add a row in the table, click in
the Name field and enter a name for the
variable, myConnection in this
example.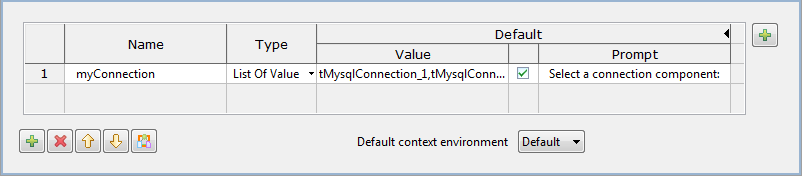
-
From the Type list field, select
List Of Value. -
Click in the Value field and then click
the button that appears in the field to open the [Configure value of list] dialog box.
-
In the [Configure value of list] dialog
box, click the New… button to open the
[New Value] dialog box, and enter the
name of one of the connection components in the text field, tMysqlConnection_1 in this example. Then click
OK to close the dialog box.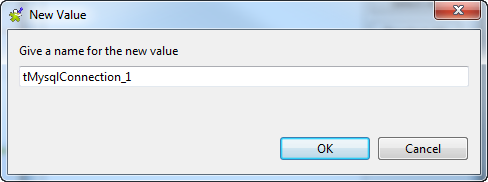
Repeat this step to specify the other connection component name as another
list item, tMysqlConnection_2 in this
example.When done, click OK to close the
[Configure Values] dialog box. -
Select the check box next to the variable value field, and fill the
Prompt field with the message you want
to display at runtime, Select a connection
component: in this example.
-
Double-click the first tMysqlConnection
component to show its Basic settings view,
and set the connection details. For more information on the configuration of
tMysqlConnection, see tMysqlConnection.Note that we use this component to open a connection to a MySQL databased
named project_q1.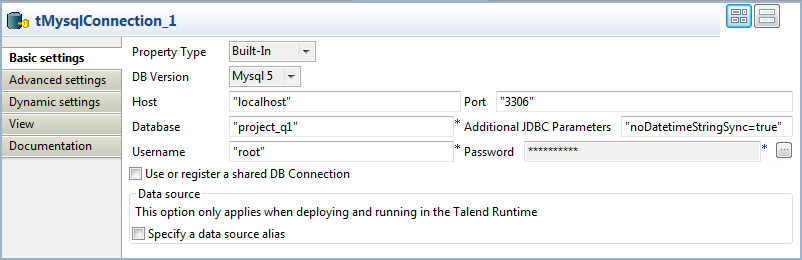
-
Configure the second tMysqlConnection
component in the same way, but fill the Database field with project_q2 because we want to use this component to open a
connection to another MySQL database, project_q2.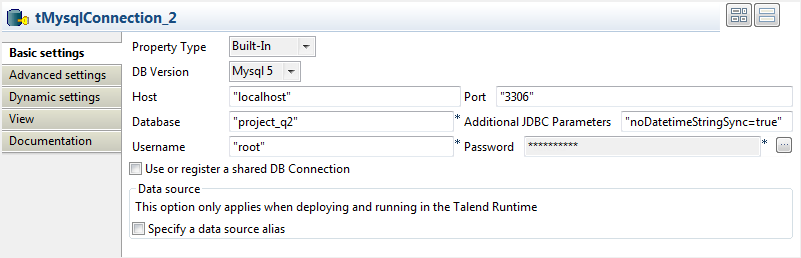
-
Double-click the tMysqlInput component to
show its Basic settings view.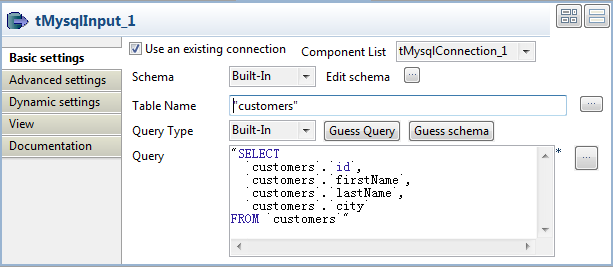
-
Select the Use an existing connection
check box, and leave the Component List box
as it is. -
Click the […] button next to Edit schema to open the [Schema] dialog box and define the data structure of the
database table to read data from.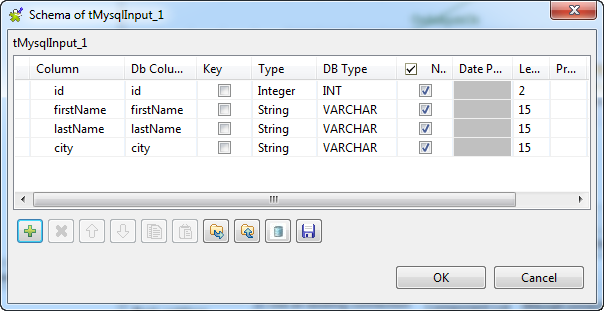
In this example, the database table structure is made of four columns,
id (type Integer, 2 characters long),
firstName (type String, 15 characters
long), lastName (type String, 15
characters long), and city (type String,
15 characters long). When done, click OK to
close the dialog box and propagate the schema settings to the next
component. -
Fill the Table field with the database
table name, customers in this example,
and click Guess Query to generate the query
statement corresponding to your table schema in the Query field. -
In the Dynamic settings view, click the
[+] button to add a row in the table,
and fill the Code field with the code
script of the context variable you just created," +in this example.
context.myConnection + "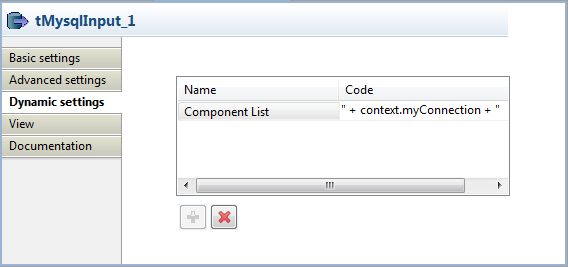
-
In the Basic settings view of the
tLogRow component, select the Table option for better display effect of the Job
execution result.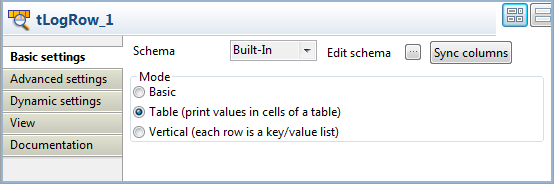
-
In the Dynamic settings view of the
tMysqlClose component, do exactly the
same as in the Dynamic settings view of the
tMysqlInput component.
-
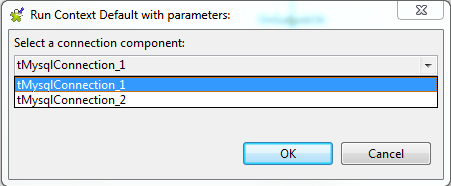
Press Ctrl+S to save your Job and press
F6 or click Run to launch it.A dialog box appears prompting you to specify the connection component you
want to use. -
Select the connection component, tMysqlConnection_1, and click OK.
The data read from database project_q1
is displayed in the Run console.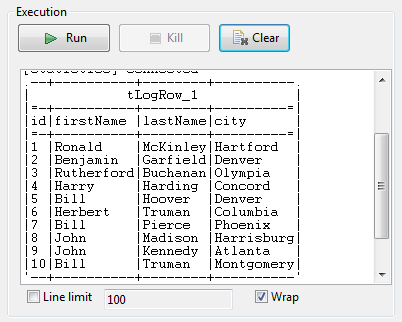
-
Press F6 or click Run
to launch your Job again. When prompted, select the other connection
component, tMysqlConnection_2, to read data
from the other database, project_q2.The data read from database project_q2
is displayed in the Run console.
Warning
This scenario makes use of the Dynamic Schema feature, which
is only available to users who have subscribed to one of the Talend solutions.
In this scenario we will read dynamic columns from a MySQL database, map them and then
write them to a table in a local output file. By defining a dynamic column alongside
known column names, we can retrieve all of the columns from the database table,
including the unknown columns.
-
Drop a tMysqlInput, a tMap and a tFileOutputDelimited component onto the workspace.
-
Link tMysqlInput to tMap using a Row >
Main connection. -
Link tMap to tFileOutputDelimited using a Row >
*New Output* (Main) connection.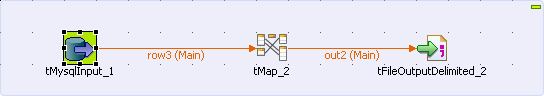
Data source and dynamic columns
-
Double-click tMysqlInput to open its
Basic Settings view in the Component tab.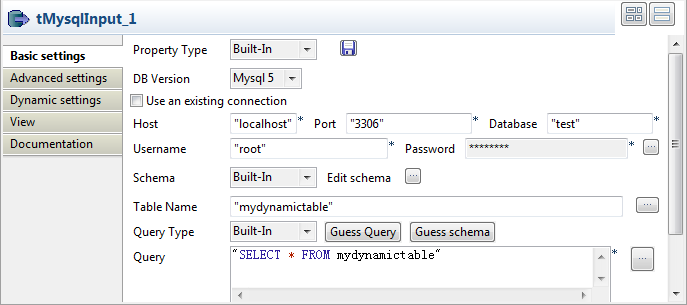
Warning
The dynamic schema feature is only supported in
Built-In mode. -
Select Built-in as the Property Type.
Select the DB Version from the
corresponding list.Next to Host, enter the database server
IP address.Next to Port, enter the listening port
number of the database server.Enter your authentication data in the Username and Password
fields. -
Set the Schema type as Built-in and click Edit
schema to define the dynamic schema.The schema editor opens:
-
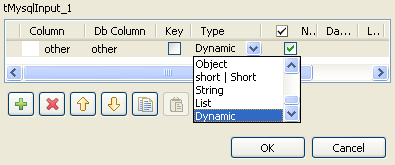
Click the [+] button to add a row to the
schema.Under Column and
Db Column, click in the fields to enter the corresponding
column names.Click the field under Type to define the
type of data.Click the arrow and select Dynamic from
the list.Warning
Under Type,
the dynamic column type must be set as Dynamic. -
Click OK to close the schema
editor. -
Next to the Table Name field, click
the […] button to select the database
table of interest.A dialog box displays a tree diagram of all the tables in the selected
database:
Click the table of interest and then click OK to close the dialog box.
-
Set the Query Type as Built-In.
In the Query box, enter the query
required to retrieve all of the columns from the table.Warning
In the SELECT statement it is necessary to use
the * wildcard character, to
retrieve all of the columns from the selected table.
-
Click tMap to open its Basic Settings view in the Component tab.
-
Click […] next to Map Editor to map the column from the source
file.
-
Drop the column defined as dynamic from the input schema on the left onto
the output schema on the right.The column dropped on the output schema retains its original
values.Warning
The dynamic column must be mapped on a one to one basis and
cannot undergo any transformations. It cannot be used in a filter
expression or in a variables section. It cannot be renamed in the
output table and cannot be used as a join condition.
-
Click OK to close the Map Editor.
Output file
-
Double-click tFileOutputDelimited to set
its Basic Settings in the Component tab.
-
Next to the File Name field, click the
[…] button to browse your directory
to where you want to save the output file, then enter a name for the
file. -
Select the Include Header check box to
retrieve the column names as well as the data. -
Save the Job.
The results below can be found after F6 is
pressed to run the Job.

As shown above, the output file is written with all the column names and
corresponding data, retrieved from the database via the dynamic schema:
Note
The Job can also be run in the Traces Debug
mode, which allows you to view the rows as they are written to the output file,
in the workspace.
For further information about defining and mapping dynamic schemas, see Talend Studio
User Guide.
For related scenarios, see: