tNLPModel
Uses an input in CoNLL format and automatically generates token-level features to
create a model for classification tasks like Named Entity Recognition (NER).
This component can run only with Spark 1.6.
tNLPModel properties for Apache Spark Batch
These properties are used to configure tNLPModel running in
the Spark Batch Job framework.
The Spark Batch
tNLPModel component belongs to the Natural Language Processing family.
The component in this framework is available in all Talend Platform products with Big Data and in Talend Data Fabric.
Basic settings
|
Define a storage configuration component |
Select the configuration component to be used to provide the configuration If you leave this check box clear, the target file system is the local The configuration component to be used must be present in the same Job. |
|
Schema and Edit Schema |
A schema is a row description. It defines the number of fields Click Sync Click Edit
The first column in the input schema must be token You can insert columns for features in between. |
|
|
Built-In: You create and store the schema locally for this component |
|
|
Repository: You have already created the schema and stored it in the |
|
Feature template |
Features: Select from the list the token-level
Relative position: This is the relative positional
For example -2,-1,0,1,2 means that you use the |
|
Additional Features |
Select this check box to add additional features in the |
|
NLP Library |
From this list, select the library to be used between If the input is a text preprocessed using the |
|
Model location |
Select the Save the model on file system check box
and either:
If you want to store the model in a specific file system, for example S3 The button for browsing does not work with the Spark tHDFSConfiguration |
|
Run cross validation evaluation |
If you select this check box, the tNLPModel will run a By default, the Fold parameter is set to
For each improvement of the model, to output the best weighted F1-score |
Usage
|
Usage rule |
This component is used as an end component and requires an input link. This component, along with the Spark Batch component Palette it belongs to, |
|
Cross validation evaluation |
The following items are output to the console of the
For each improvement of the model, the best weighted F1-score is output For more information on the log4j logging levels, see the Apache |
|
Spark Batch Connection |
In the Spark
Configuration tab in the Run view, define the connection to a given Spark cluster for the whole Job. In addition, since the Job expects its dependent jar files for execution, you must specify the directory in the file system to which these jar files are transferred so that Spark can access these files:
This connection is effective on a per-Job basis. |
Generating a classification model
This scenario applies only to subscription-based Talend Platform products with Big Data and Talend Data Fabric.
This Job uses text data divided into tokens in CoNLL format to train a classification
model, design features and evaluate the model.
You can find more information about natural language processing on
Talend Help Center (https://help.talend.com).
Creating a Job to generate a classification model
entities from manually annotated tokens in CoNLL format.
-
Drop the following components from the Palette onto the
design workspace: tFileInputDelimited and
tNLPModel. - Connect the components using Row > Main connections.

Selecting the Spark mode
Depending on the Spark cluster to be used, select a Spark mode for your Job.
The Spark documentation provides an exhaustive list of Spark properties and
their default values at Spark Configuration. A Spark Job designed in the Studio uses
this default configuration except for the properties you explicitly defined in the
Spark Configuration tab or the components
used in your Job.
-
Click Run to open its view and then click the
Spark Configuration tab to display its view
for configuring the Spark connection. -
Select the Use local mode check box to test your Job locally.
In the local mode, the Studio builds the Spark environment in itself on the fly in order to
run the Job in. Each processor of the local machine is used as a Spark
worker to perform the computations.In this mode, your local file system is used; therefore, deactivate the
configuration components such as tS3Configuration or
tHDFSConfiguration that provides connection
information to a remote file system, if you have placed these components
in your Job.You can launch
your Job without any further configuration. -
Clear the Use local mode check box to display the
list of the available Hadoop distributions and from this list, select
the distribution corresponding to your Spark cluster to be used.This distribution could be:-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Yarn client
-
Yarn cluster
-
-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Standalone
-
Yarn client
-
Yarn cluster
-
-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Yarn client
-
-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Yarn client
-
Yarn cluster
-
-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Standalone
-
Yarn client
-
Yarn cluster
-
-
For this distribution, Talend supports:
-
Yarn cluster
-
-
Cloudera Altus
For this distribution, Talend supports:-
Yarn cluster
Your Altus cluster should run on the following Cloud
providers:-
Azure
The support for Altus on Azure is a technical
preview feature. -
AWS
-
-
As a Job relies on Avro to move data among its components, it is recommended to set your
cluster to use Kryo to handle the Avro types. This not only helps avoid
this Avro known issue but also
brings inherent preformance gains. The Spark property to be set in your
cluster is:
1spark.serializer org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializerIf you cannot find the distribution corresponding to yours from this
drop-down list, this means the distribution you want to connect to is not officially
supported by
Talend
. In this situation, you can select Custom, then select the Spark
version of the cluster to be connected and click the
[+] button to display the dialog box in which you can
alternatively:-
Select Import from existing
version to import an officially supported distribution as base
and then add other required jar files which the base distribution does not
provide. -
Select Import from zip to
import the configuration zip for the custom distribution to be used. This zip
file should contain the libraries of the different Hadoop/Spark elements and the
index file of these libraries.In
Talend
Exchange, members of
Talend
community have shared some ready-for-use configuration zip files
which you can download from this Hadoop configuration
list and directly use them in your connection accordingly. However, because of
the ongoing evolution of the different Hadoop-related projects, you might not be
able to find the configuration zip corresponding to your distribution from this
list; then it is recommended to use the Import from
existing version option to take an existing distribution as base
to add the jars required by your distribution.Note that custom versions are not officially supported by
Talend
.
Talend
and its community provide you with the opportunity to connect to
custom versions from the Studio but cannot guarantee that the configuration of
whichever version you choose will be easy. As such, you should only attempt to
set up such a connection if you have sufficient Hadoop and Spark experience to
handle any issues on your own.
For a step-by-step example about how to connect to a custom
distribution and share this connection, see Hortonworks.
Configuring the connection to the file system to be used by Spark
Skip this section if you are using Google Dataproc or HDInsight, as for these two
distributions, this connection is configured in the Spark
configuration tab.
-
Double-click tHDFSConfiguration to open its Component view.
Spark uses this component to connect to the HDFS system to which the jar
files dependent on the Job are transferred. -
If you have defined the HDFS connection metadata under the Hadoop
cluster node in Repository, select
Repository from the Property
type drop-down list and then click the
[…] button to select the HDFS connection you have
defined from the Repository content wizard.For further information about setting up a reusable
HDFS connection, search for centralizing HDFS metadata on Talend Help Center
(https://help.talend.com).If you complete this step, you can skip the following steps about configuring
tHDFSConfiguration because all the required fields
should have been filled automatically. -
In the Version area, select
the Hadoop distribution you need to connect to and its version. -
In the NameNode URI field,
enter the location of the machine hosting the NameNode service of the cluster.
If you are using WebHDFS, the location should be
webhdfs://masternode:portnumber; WebHDFS with SSL is not
supported yet. -
In the Username field, enter
the authentication information used to connect to the HDFS system to be used.
Note that the user name must be the same as you have put in the Spark configuration tab.
Configuring the input component
-
You annotated the named entities in the CoNLL files to be used for training
the model.
-
Double click the tFileInputDelimited component to open
its Basic settings view and define its properties.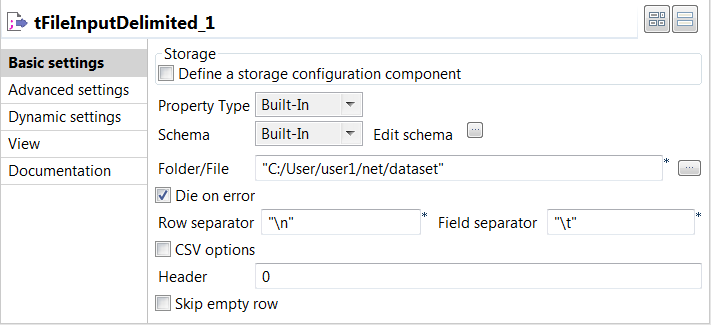
-
Set the Schema as Built-in and click
Edit schema to define the desired
schema.The first column in the output schema must be
tokens and the last one must be
labels. In between, you can have columns
for features you added manually. -
In the Folder/file field, specify the path to
the training data. - Leave the Die on error check box selected.
-
Set the Schema as Built-in and click
-
In the Advanced settings view of the
component, select the Custom encoding check box if you
encounter issues when processing the data.
-
From the Encoding list, select the encoding
to be used, UTF-8 in this example.
Evaluating and generating a classification model
evaluate and generate a classification model.
-
Double click the tNLPModel component to open its
Basic settings view and define its properties.
-
Click the [+] button under the
Feature template table to add rows to the
table. -
Click in the Features column to select the
features to be generated. -
For each feature, specify the relative position.
For example -2,-1,0,1,2 means that you use the
current token, the preceding two and the following two context
tokens as features. -
From the NLP Library list, select the same
library you used for preprocessing the training text data.
-
Click the [+] button under the
-
To evaluate the model, select the Run cross validation
evaluation check box. -
Select the Save the model on file system and the
Store model in a single file check boxes to save the
model locally in the folder specified in the Folder
field. - Optional:
Change the logging output level for the execution of the Job to output the best
weighted F1-score for each improvement of the model in the
Run view:-
In the Run view, click the Advanced
settings tab. -
Select the log4jLevel check box, and select
Info from the list.
-
In the Run view, click the Advanced
-
Press F6 to save and execute the
Job.
Info, the best weighted F1-score is output to the console of
the Run view for each improvement of the model.
The following
items are also output to the console of the Run
view:
| Category | Item |
|---|---|
| For each class | The class name |
| True Positive: the number of elements that were predicted correctly as elements of this class. |
|
| Predicted True: the number of elements that were predicted as elements of this class. |
|
| Labeled True: the number of elements belonging this class. |
|
| Precision score: this score varies from 0 to 1 and indicates how relevant the elements selected by the classification are to a given class. |
|
| Recall score: this score varies from 0 to 1 and indicates how many relevant elements are selected. |
|
| F1-score: the harmonic mean of the Precision score and the Recall score. |
|
| For the best model | The global weighted F1-score |
The model file is stored in the specified folder. You can now use the
generated model with the tNLPPredict component to predict named
entities and label text data automatically.